What is an Application Delivery Controller?
Just when you think you have a good handle on the key technologies on the market, they come up with something new. If you’ve been told that you need to look at putting in an application delivery controller (ADC), read on.
Glorified Load Balancer?
To get to the heart of the matter, we need to figure out exactly what an application delivery controller is. If you were under the impression that it’s just a dressed-up load balancer, you would not be exactly right. An ADC does server load balancing, but not just that. It does much more.
What’s in a name? Sometimes the terminology changes because the technology is just not the same anymore. A noun may describe a person, place, or thing, but to name it properly — unless you want to choose some arbitrary name like Alphabet, as Google did for its new company formation — it helps to think about what the noun actually does. A writer writes. A coder codes. And a load balancer balances loads. But what if you want it to accelerate applications too? Would it still be a load balancer?
The transition from load balancer to application delivery controller was a natural one. If a writer started doing coding, plus a bit of tech service, he might want to rebrand himself as a tech entrepreneur. An application delivery controller balances traffic loads. But it would be a misnomer to call it simply a load balancer. What else does it do?
Some Definitions
TechTarget offers a pretty good definition: “An application delivery controller (ADC) is a network component that manages and optimizes how client machines connect to web and enterprise application servers.” Managing traffic is a fairly important part of keeping the internet running. And just like a traffic cop or traffic signal instructs the driver as to when and which way to travel, an ADC points the way for data packets as they enter and leave a server environment.
The basic diagram below gives us some idea of the placement and role of the ADC within the IT infrastructure. “The term controller, in this context, is the function of managing (or controlling) the flow of data between computing systems.” It is a necessary go-between to optimize the user experience.
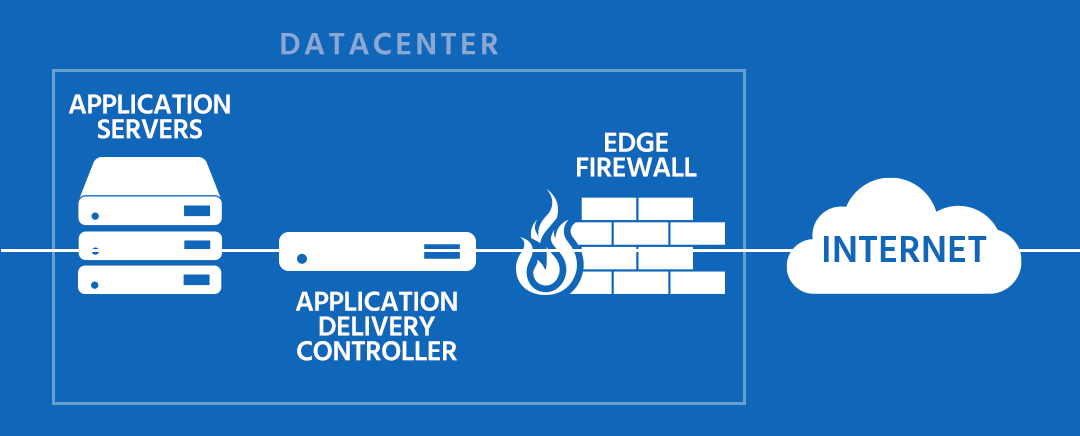
The whole concept of application delivery has been developing over the past decade of so. There was a time when the main issue in maintaining a network environment was keeping the connections up and running. But we’ve moved way past that. The transmission of packets, basically layers 1-4 of the OSI model, is fast and reliable these days. The main issue now is to ensure that applications are successfully and securely delivered as quickly as possible.
So another definition becomes important here: application delivery networking. According to A10 Networks, “Application delivery networking is the practice of creating a framework of technologies that work together to provide the appropriate levels of availability, security, visibility, and acceleration to networked applications.’ Now we are talking about maintaining a whole ecosphere of software assurance — not just balancing traffic loads.
What an ADC Does
We already said an ADC does load balancing. Everybody knows that. But did you know that it can also fight off DDoS attacks and analyze the health of your application? But before we leave the topic of load balancing, we should clarify just what services an ADC provides in its role as a traffic load balancer.
Availability is everything. If your connection or application is not available, it doesn’t matter how many bells and whistles it has.
Availability is everything. If your connection or application is not available, it doesn’t matter how many bells and whistles it has. A load balancer will cleverly distribute or redirect the traffic flow to make sure that an application keeps doing what it’s supposed to do. Load balancing works hand-in-hand with failover to guarantee application uptime.
Two other key aspects of load balancing are scalability and performance. If you don’t think that load balancing is important, wait to you get a big spike in traffic on a good day and see how well your application without load balancing does. It’s a good way to lose customers. To learn more, see our post “What Is Load Balancing — And Do I Need It? ”
Probably the next most important capability of an ADC is application acceleration. What is it? Well, it’s definitely something you would expect in an optimized application delivery network. To accelerate means to increase in extent or speed. Users want applications to do more, and they want them to do it better and faster. According to F5, “Application acceleration uses a number of technologies to improve application performance and response time over network connections.” It’s really a broader term that includes a variety of functions, like SSL offloading, smart caching, and intelligent compression.
In a sense, there’s no limit to what the ADC can do. It’s in a good position in the network, so whenever designers and engineers think up another helpful function, why not just put it into the ADC? We don’t need individual physical devices for every task anymore. That’s why the ADC is also a very good place to do network security. You can put your web application firewall in there, and you can even use it for intrusion detection.
ADC Features
An application delivery controller can come in different form factors. It can exist as a dedicated piece of equipment. An ADC can be a virtual device on the cloud. Or it can come as a software-only solution.
The list of features will vary from vendor to vendor. Here are some of them:
- Automatic application health checks
- Proxy and reverse proxy
- SSL Offload
- Caching
- Data compression
- TCP multiplexing
- Traffic shaping
- Web application firewall
- DNS firewall
- DDoS protection
- AAA server
Notice that many of these features can be viewed as belonging to the function categories already discussed: load balancing, application acceleration, and security. It should be clear by now that an ADC does a whole lot more than just load balancing.
Conclusion
An application delivery controller offers a single point of control. Using a single device for so many capabilities means that we keep learning how to do more with less. According to Distil Networks, demand for ADC technology is on the rise. They cite an August 2016 Gartner report that called ADCs “a key component within enterprise and cloud data centers to improve application availability, performance and security”. The ADC is an important addition to modern networks. Have you installed yours yet?
 What is an Application Delivery Network?
What is an Application Delivery Network?  Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB)
Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB)  Measuring Failure
Measuring Failure